Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS)
What is chorionic villus sampling?
Chorionic villus sampling (CVS) is a test which involves obtaining a small sample of tissue, the “chorionic villi” from the developing placenta of a pregnant woman. The placenta usually has the same makeup as the baby and can be tested for chromosomal or DNA abnormalities such as Down syndrome.
Ultrasound Care’s team of specialist Obstetricians, Genetic Counsellors and sonographers are experts in providing CVS for pregnant women.
What women may be offered CVS?
Most testing by CVS is offered to pregnant women who are at particular risk of chromosomal abnormality such as Down syndrome. This could include:
- Women who have shown an increased chance of a chromosome condition on a cell free fetal DNA test (NIPT).
- Women who have shown an increased chance on a nuchal translucency test.
- Women over the age of 35.
- Women who have had a previous affected baby or pregnancy.
- Parents who are known to have a chromosomal abnormality themselves.
- Parents who are known to be a genetic carrier themselves.
- Parents who are known to be at risk of having a baby with one or a number of rare “metabolic” disorders.
Occasionally, CVS is performed for women who are particularly anxious about the risk of chromosomal abnormality.
How is the CVS test performed?
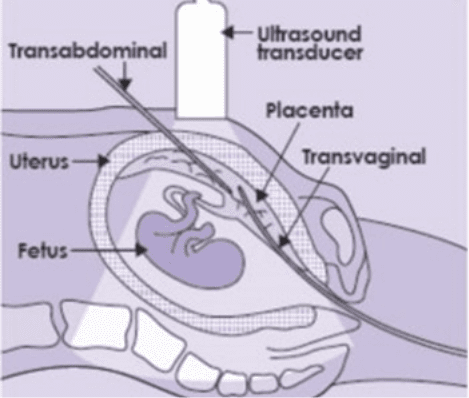
A CVS is performed either trans-abdominally or trans-cervically.
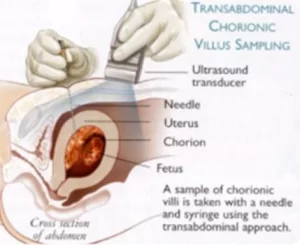 For a trans-abdominal CVS, the Ultrasound Care team cleanse the skin of the lower with an antiseptic alcohol-based solution, and the skin and underlying tissues are injected with local anaesthetic.
For a trans-abdominal CVS, the Ultrasound Care team cleanse the skin of the lower with an antiseptic alcohol-based solution, and the skin and underlying tissues are injected with local anaesthetic.
Women who have had a CVS describe the discomfort felt during the injection of the local anaesthetic is similar to that felt when blood is drawn from the forearm. With ultrasound control, your Ultrasound Care Obstetrician guides a fine needle into the placenta and placental tissue (chorionic villi) is then aspirated (withdrawn).  Sometimes, women experience a dragging sensation in the pelvis or in the legs during the procedure and this should be expected, and in some instances, more than one biopsy is required.
Sometimes, women experience a dragging sensation in the pelvis or in the legs during the procedure and this should be expected, and in some instances, more than one biopsy is required.
 If your scan shows that the placenta is developing on the back uterine wall and low in the uterus it may be easier for your Ultrasound Care obstetrician to perform the CVS procedure trans-cervically. In this case, a speculum is inserted into the vagina and the cervix is cleansed with an antiseptic solution.
If your scan shows that the placenta is developing on the back uterine wall and low in the uterus it may be easier for your Ultrasound Care obstetrician to perform the CVS procedure trans-cervically. In this case, a speculum is inserted into the vagina and the cervix is cleansed with an antiseptic solution.
A special catheter is then guided into the placenta with the help of ultrasound, and placental tissue is gently aspirated. A trans-cervical CVS procedure is usually completely painless. A small amount of bleeding is relatively common. This image shows the catheter coming up through the cervix and into the placenta which is on the back wall of the uterus.
When is the CVS test performed?
Ideally the test is performed between 11-12 weeks gestation. However, it can be performed as early as 11 weeks and as late as 40 weeks.
What preparation do I need before the test?
It is preferable for you to attend for your CVS with a moderately full bladder. This brings the uterus up into the abdominal cavity and makes the placenta more easily accessible for the test.
However, if you begin to feel very uncomfortable with a full bladder then your Ultrasound Care team will ask you to try to let some urine out as this may also hinder the test.
As part of the CVS testing, we may also need to take a blood sample from you and your partner for the laboratory.
It is also very important to know what your blood group is before the CVS test i.e., Rhesus (Rh) positive or negative. If possible, please ask your referring doctor to provide this information or bring along you blood group card to Ultrasound Care at the time of the test.
Please note, if you have a Rhesus negative blood group you will need an injection of anti-D after the test. This will be explained further by your Ultrasound Care Obstetrician at the time of your CVS.
Why is an ultrasound required before a CVS?
An ultrasound scan is performed before the CVS test to:
- Check gestational age
- Determine whether there are twins or more
- Check for major abnormalities in the baby
- Locate the placenta
What happens to the sample after it has been taken?
The specimen is sent to the laboratory and processed that day. There are generally two ways the placental tissue is assessed, and both are highly accurate.
Limited information on chromosome 21, 18, 13 and X and Y is available in 1-2 days. Every cell should contain 23 pairs of chromosomes and each pair is examined. This information takes 10-14 days.

The individual bands of each chromosome can be examined in great detail for subtle genetic abnormalities such as:
- Insertion of genetic material into a chromosome
- Deletion of genetic material from a chromosome
- Exchanging of genetic material between chromosomes (called translocations).
The CVS test is used to help exclude not only Down syndrome but a wide variety of additional subtle and major chromosome abnormalities. There is more detail about the laboratory tests later in this article.

What are the risks of the CVS test?
There is less than 0.5% (1:200) risk of miscarriage with the CVS test. The pre-existing background risk of miscarriage is approximately 2% at this gestation. This suggests that the added risk of the CVS procedure is small, relative to the general risk of miscarriage at this stage of pregnancy.
To minimize the risk of infection, the Ultrasound Care team follow strict sterile techniques.
During the CVS, the needle itself stays outside the gestation sac, so the fetus is never touched. The sample is taken from the chorionic villi which lie outside the gestation sac.
What should I expect after the CVS test?
It is recommended that you rest for the remainder of the day after your CVS. Many women feel tired and emotional and can be a little bit sore in the belly. This does not mean you should confine yourself to bed, and if you feel well enough to go back to work this is fine, but you should avoid any strenuous activity like lifting heavy weights.
Most women will experience a short duration of mild crampy period-like pains, lower abdominal pains or even leg pains after the test. This is most likely to occur after the local anaesthetic wears off, i.e., within the first half hour after the test. Some women may experience slight vaginal blood spotting after the test which is also not unusual.
Your Ultrasound Care doctor will ask you to stay for 10-15 minutes to recover after you CVS, and the Ultrasound Care team will give you a list of things to look out for after the procedure. Remember that a small amount of spotting is quite common as we have taken a placental biopsy.
When should I be concerned of miscarriage after a CVS?
Warning signs of miscarriage include strong period like pains with fresh red bleeding. Call Ultrasound Care or your referring doctor if you are concerned.
If a miscarriage does occur due to the procedure, you will usually suffer symptoms in the first 24-48 hrs after the test.
If you are worried at any time about your fetus after your CVS, please call our team as you are welcome to come in for an ultrasound to check the fetal heart motion.
The CVS laboratory tests
(CMA) testing
 In order to get faster results, the laboratories have developed a technique called fast Fluorescent In-Situ Hybridization, where some of the cells from the sample are stained with a fluorescent dye.
In order to get faster results, the laboratories have developed a technique called fast Fluorescent In-Situ Hybridization, where some of the cells from the sample are stained with a fluorescent dye.
This can give us results for chromosomes 13, 18, 21, X & Y, in 24 hours. This is especially reassuring for women who have had a concerning result on their screening test for Down syndrome (trisomy 21).(CMA) testing
 Chromosome microarray (CMA) testing is a detailed genetic test which can detect extra or missing segments of DNA. As there are usually two copies of each chromosome, there should be two copies of each segment of DNA.
Chromosome microarray (CMA) testing is a detailed genetic test which can detect extra or missing segments of DNA. As there are usually two copies of each chromosome, there should be two copies of each segment of DNA.
Using the chorionic villus sample the microarray can look for a variation in the number of copies of genes. This is known as a copy number variant. If the test finds a copy number variant, the laboratory will check which genes are duplicated or missing from this information, and we can then predict what sort of problems the baby may have. Remember that we all vary, so Ultrasound Care will usually send samples of blood from parents to help the laboratory understand whether the copy number variant is inherited. This helps us determine the significance of the copy number variant for your baby. Using special procedures in the laboratory, cells are grown in a culture medium. The cells are then fixed and stained.
Using special procedures in the laboratory, cells are grown in a culture medium. The cells are then fixed and stained.
With high power microscopy the chromosomes in these cells can be examined and in this way it is possible to find out if the baby has Down syndrome, or any of the other known less common chromosome problems. This is called a karyotype. We can also look at the chromosomes to determine the sex of your baby.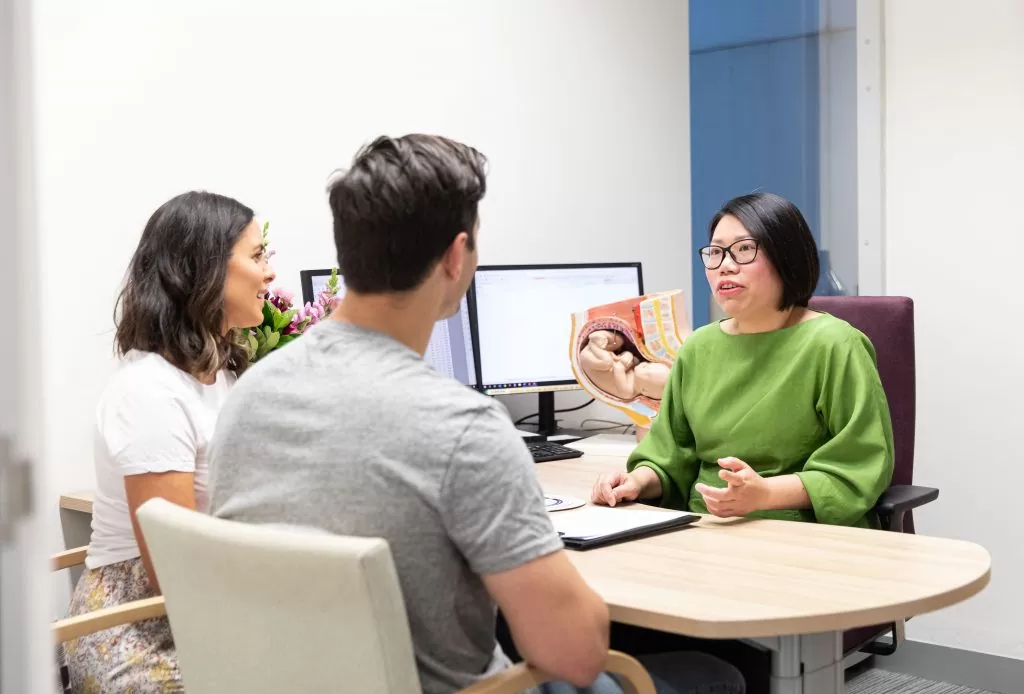
When are you informed of the CVS results?
The Ultrasound Care team will usually ring you with the CVS results as soon as they become available, and we also forward them to your referring doctor.
Fast FISH/DNA PCR results are available in 24-48 hours. The full karyotype usually takes 10-14 days; microarrays usually take 5-10 days, and our team will call with all of your results whether they are normal or not. You are always welcome to come and see one of the specialists, geneticists or genetic counsellors to talk further, and we will help you to understand what the results mean for the pregnancy and whether other tests are recommended.
Issues with test results
Occasionally there are problems with the sample; it may fail to grow, or it may give a confusing result. These problems are uncommon and only occur in <1% of all CVS tests done by Ultrasound Care.
If this does occur, our team will contact you and discuss what you should do next. We sometimes will need to test you and your partner to see if one of you has a similar chromosomal pattern. If further testing is necessary, you still have the choice of an amniocentesis test at 15-16 week of pregnancy to clarify the situation and your Ultrasound Care team will explain this to you.





