Non Invasive Pre-Natal Testing (NIPT/NIPS)
Non-invasive prenatal screening (NIPS) or Cell free fetal DNA (cfDNA)
There are a number of non-invasive options available to pregnant women that provide information on the fetus. For women concerned about their pregnancy and wanting further information, Ultrasound Care provides NIPT/NIPS.
What is non-invasive prenatal screening (NIPS) or Cell free fetal DNA (cfDNA)?
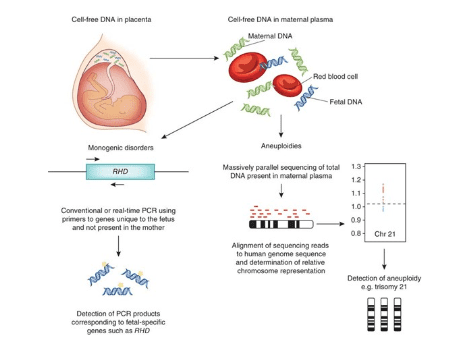
Free fetal DNA from the pregnant woman’s blood is collected and fetal DNA is tested for extra fragments of chromosomes. The most common chromosomal anomaly is an extra copy of chromosome 21. If extra fragments of chromosome 21 are detected this may signify the presence of Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome) in the fetus.
Cell free fetal DNA can also assess the fragments of other chromosomes including the sex chromosomes, so it can tell you the sex of the fetus (if you wish to know it). With the improvement of technology, the test has expanded, and some tests can now assess the amount of fragments of all the chromosomes and some large sub-sections of the chromosomes.


Cell free fetal DNA is reported to have a detection rate of 99% for Down syndrome.
A few important points about the test are:
- It is not 100% diagnostic, so it is really a screening test.
- It has a better detection rate than any other screening test we have, such as nuchal translucency screening, combined nuchal and serum screening and the triple test.
- It can be done from 10 weeks gestation onwards.
- It is suitable for twin and some triplet pregnancies.
What if the result is returned as “high risk”
If your result is “high risk” this means that the laboratory has found more or less DNA fragments than expected and a confirmatory test like a chorionic villus sampling or amniocentesis is necessary.
The Ultrasound Care team will then recommend a scan to look at the baby structure to help us guide which confirmatory test is more suited to you. Some chromosome conditions are more suited to an amniocentesis because of the chance of a confusing result from confined placental mosaicism (the chromosomal defect being confined to the placenta but not present in the baby). During your consultation and scan, our Obstetricians and Genetic Counsellor team will talk you through your results and discuss which tests are suitable for you.

Cell free fetal DNA has become a common test
This test is extremely popular either
- As a primary screening test for Down syndrome and other trisomies
- As a follow-up test after nuchal translucency screening
Even if the cell free fetal DNA test (NIPT) result is “low risk”, Ultrasound Care will still recommend an ultrasound examination at 12-14 weeks gestation to confirm the gestational age, detect the presence of twins, and to look for major structural abnormalities which may be obvious in the early stages of pregnancy.
We will also recommend an ultrasound examination at 19-20 weeks gestation to detect structural abnormalities which may become obvious as the baby matures, and to determine the position of the placenta and the volume of amniotic fluid around the baby.
Ultrasound Care’s team of specialist Obstetricians and Genetic Counsellors specialise in prenatal diagnose and ultrasound.
If you would like to discuss this option for your pregnancy, we have locations all around Sydney, please call us at a practice most convenient to you and make an appointment to see one of our specialist Obstetricians or Genetic Counsellors.





